[Adaptive Transformers for Robust Few-shot Cross-domain Face Anti-spoofing]
Recent Face anti-spoofing methods perform well under the intra-domain setups. For Robust performance, dataset should contain larger appearance variations of images with complex scenes with different sensors.
Author proposed adaptive vision transformers for robust cross-domain face anti-spoofing. Using ViT as a Backbpone, introducing ensemble adapters module and feature-wise transformation layers.
Introduction
Face authentication is mainly applied to controlled scenarios with fixed sensors. Face images may be acquired from wider angles, complex scens and different devices, which can be regraded as a set of mixed data domains.
Existing method use intra-database testing and cross-datatbase testing to evaluate the intra-domain and cross-domain face anti-spoofing. The former one trains and evaluates models on data split from the same database, while the latter one does from different databases.
Recent methods have already shown saturated performance on intra-database evaluations in well controlled scenarios. Although significant profress has been made, existing methods do not perform well on cross-dataset tests.
There are a few challenges for cross-domain face anti-spoofing applications:
- Domain gap : The domain gap is highly correlated to the key factor of recognizing spoof: visual appearance. Spoofing cures can dramatically change or disappear with different camera devices, illuminations and image resolutions.
- Limited Data : Compared to datasets for other vision tasks, commonly used datasets for face anti-spoofing are considerably smaller in scale. Models trained with limited data can easily over-fit the training data. Therefore, the model generalize poorly to other domains.
The main contributions of of this work are:
- Proposed adaptive transformers with ensemble adapters and feature-wise transforms for robust cross-domain face anti-spoofing with a few samples.
- Achieve state-of-the-art cross-domain face anti-spoofing results on widely-used benchmark datasets. This Closes the gap between intra database evaluation and performance in real-world applications
- Conduct in-depth analysis of adaptive transformers and show model explainability with insights for face anti-spoofing.
Related Work
Face Anti-spoofing Early work exploits spontaneous human behavior or predefined movements to address face interaction. Due to clear weakness in video playing attacks and inconvenience from user interaction, recent approaches evolve into modeling material properties. Recently deep neural networks have been applied to anti-spoofing and acheived state of the art performance than conventional methods
As limited spoof data is available for learning classifiers or deep neural networks, auxiliary supervisory signals have been introduced to infuse the models with prior knowledge. To improve model interpretability. feature disentanglement is proposed along with the advances in the gnerative adversarial networks
A model based on a vision transformer is proposed to detect spoofing attack. This work propose an adaptive transformer model to robustly handle challenging print and replay attacks across different datasets using a few-shot setting.
Domain generalization Domain generalization for face anti-spoofing aims to learn a model from multiple source datasets, and the model should generalize to the unseen target dataset. Several approaches based on adverarial training and triplet loss have been developed to learn a shared feature space for multiple source domains that can be generalized to the target domain. Meta-learning formulation are exploited to simulate the domain shift at training time to learn a representative feature space.
The paper tackle a real-world anti-spoofing problem when only a few images are available from target datasets. The paper propose an effective cross-domain few-shot framework based on an adaptive transformer that achieves state-of-the-art performance
Few-shot Learning Few-shot learning methods aim to adapt models to novel classes from a few samples from each class. Cross-domain few-shot learning further addresses the problem when the novel classes are sampled from a different domain with different data distribution.
Anti-spoofing methods based on few-shot and zero-shot learning are proposed to detect multiple spoof attacks. Cross-domain model performance is unstable under different protocols.
The paper proposed learn features from balanced data from the source domains and a few samples from the target domain. The paper also propose a adaptive transformer based on a adapter and a feature-wise transformation to improve model stability.
Model
In the work, the paper assume using multiple dataset which have different doamins and one target dataset. Each source dataset consist of real and fake data. The goal of few-shot cross-domain anti-spoofing is to learn a classification model that generalize to the target domain by accessing source datasets as well as a few samples from the target set.
Vision Transformer
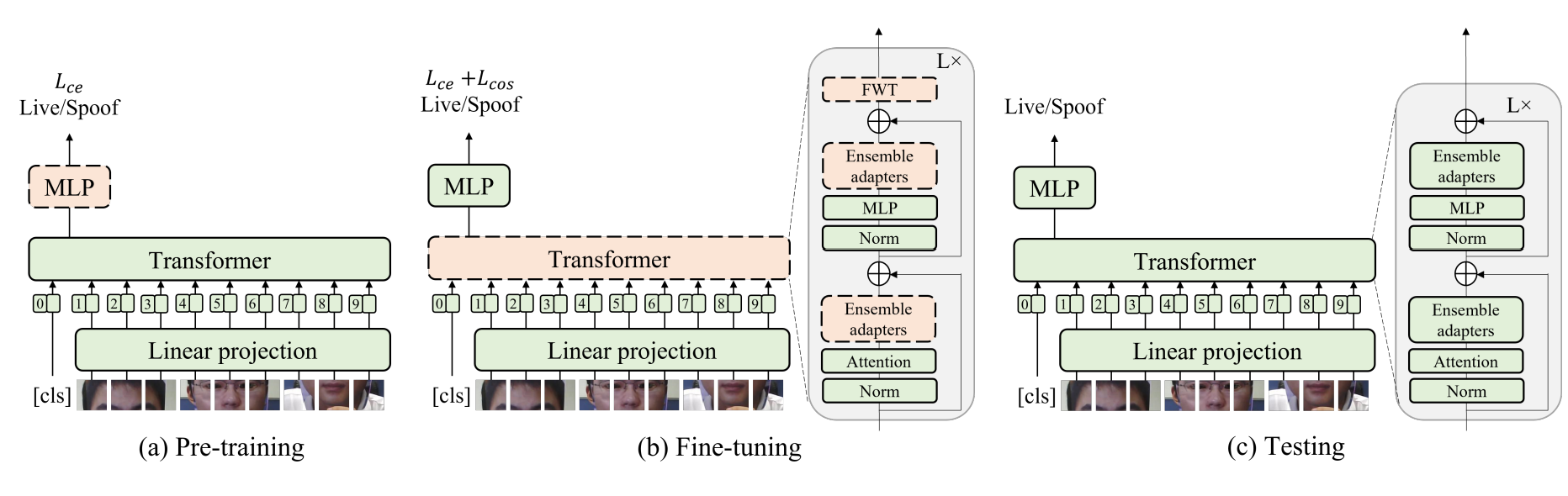
The paper adopt the vision transformer as the backbone module. The input image is split and reshaped into a sequence of flattened 2D patches. For positional encoding, the paper used learnable positional embedding to the patch embedding. The paper use ViT to obtain the image representation and a multiple perceptron head to get the classification prediction.
At each training iteration, sample the same amount of live and spoof images from source domain and a small set of target domain. For training cross entropy loss is used and defined as below.
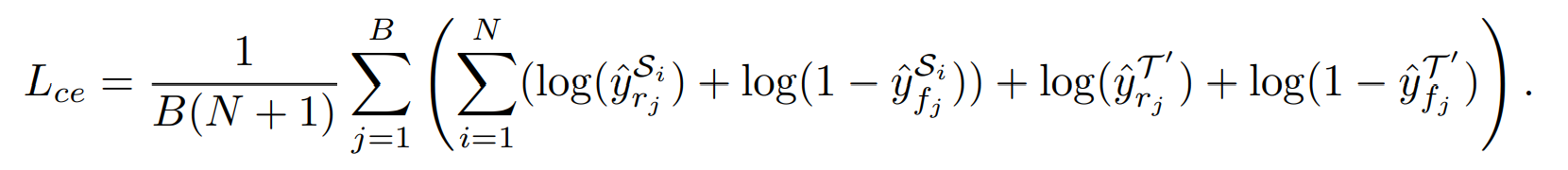
The B is the Sample size, N is the Source Domain, and y is a prediction. S is the domain for source, and T is for target. r is real, and f is false.
Ensemble Adapter
The basic transfer learning strategy is to train a classifier on top of features extracted by a backbone network pretrained on ImageNet using anti-spoofing data. However, this gives poor performance on the face anti-spoofing task.
- The backbone pretrained using a generic dataset cannot adapt well on the specific anti-spoofing facial data.
- Features extracted from the pre-trained backbone network are high-level. Therefore it is not suitable for the face anti-spoofing task which needs to varify the difference between the low-level information.
Fine-tuning a classifier and the backbone on anti-spoofing data result in a better result. However, the good performance is limited on the source domain. The performance on the target domain becomes unstable.
The paper predicts the instability comes from two factors.
- When fine-tuning large models with few samples, the catastrophic forgetting problem usually causes training instability.
- The domain gap between the target samples and the source domain is large such that the target samples are close to the decicion boundary and have high uncertainty.
The basic solution to this problem is to freeze a majority of the backbone and partially fine-tune the network. The approach with fine-tuning only top layers of backbone networks does not address this issue.
Adaptive module
In NLP, the adapterBERT has been shown to successfully transfer the pre-trained BERT model to vairous downstream tasks without re-training the whole network. Similarly, the paper introduce the adapter layer to alleviate the instability issue.
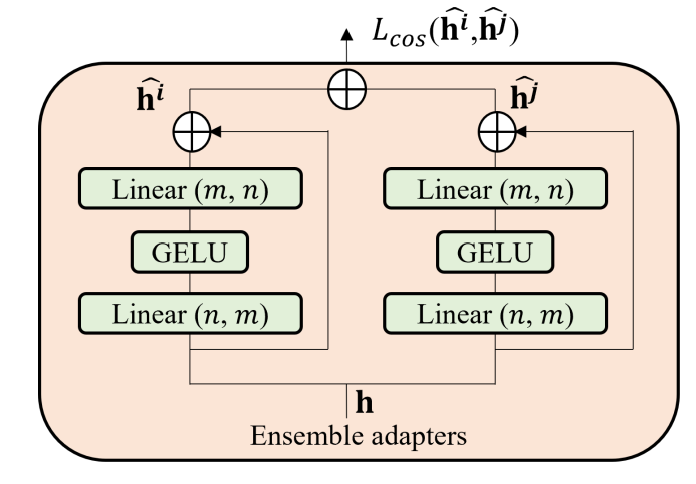
As shown in the above images, the adapter has a bottleneck architecture. It projects the n-dimensional features into lower dimension m, applies non-linear activation function GELU, the project back to n dimensions.
The Adapter contains the skip connection. Thus, if the parameter of the projection head are initialized to near-zero, the adapter is nearly an identity function.
As shown in the overview of the model structure, two adaptive modules are inserted into each transformer block. During the fine-tuning stage, the paper fix the original transformer back-bone and update the weights of adaptive modules. As adapter contains only a few parameters, they can be learned without optimization difficulites.
Since the adapters contain a skip-connections, they generate representation with less deviation from the pre-trained models. With less deviation, the adapter alleviate the catastrophic forgetting problem, improving training stability.
Adapter help adjust the feature distribution of the pre-trained transformer blocks to the face anti-spoofing data, maintaining the discriminative strength and good generalization ability of pre-trained transformer representation.
Ensemble adapters and cosine similarity loss.
The ensemble adapter module achieve higher accuracy and minimize training instability issues. The paper replace the naive adapters with ensemble adapter modules. The ensemble adapters contains K adapters in parallel. In each ensemble adapter modules, the representation h is the input to K adapters and the outputs of adapters h^k are aggregated and forwarded to the next layer.
Multiple adapters learn repetitive information by simply ensembling the outputs. This result in not improving the discriminability of the features and leading to limited performance improvements.
In order to learn diverse features from multiple adapters, the paper use cosine similarity loss. The consine loss enforces the outputs of the adapters to be dissimilar to each other and help learn diverse features.
The Cosine loss is defined as follows.
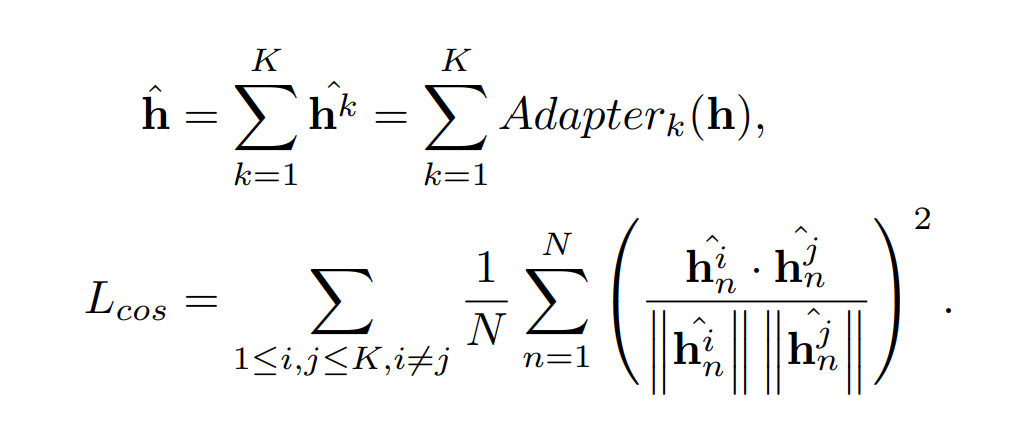
In this formula, the paper assume the input image has N tokens and the feature dimension is D.
Feature-wise Transformation
The goal is to learn a model that generalize well to the target domain using source datasets and a small subset of the target dataset. Due to the distribution mismatch of the source and target domains and limited target domain data during training, the model is prone to over-fitting.
The paper include a feature-wise transformation layer into the transformer blocks. The scaleing and biase terms of affine transformations sample from Gaussian distribution.
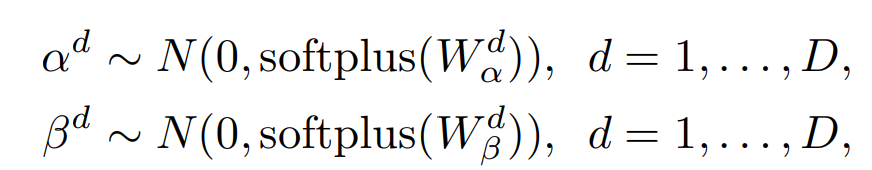
The W denote learnable sampling hyper parameters, and D denotes the channel dimensions of the activation map of each transformer block. Then apply the sampled affine transformation to intermediate features as follows.
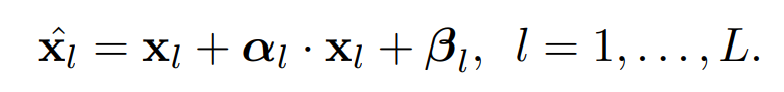
In practice the same affine transformation is applied across all patch embeddings.
The paper insert FWT layer in each trasnformer block. The FWT layer is used only at traning and not used in testing. FWT is used to serve as feature-level data-augmentation to increase the diversity of traning samples. This dramatically reduce overfitting and improve stability and performance.
Adaptive Transformer
The proposed adaptive transformer consists of three stages: pre-training, fine-tuning and testing.
- Pre-training : fix ViT backbone initialized with pre-trained weights form ImageNet and train the MLP head using the binary cross entropy.
- Fine-Tuning : Two ensemble adaptor modules and an FWT layers to each transformer block. Train all ensemble adaptors and FWT layers with all the other weights fixed until convergence using cross entropy loss and cosine loss.
- Testing : Remove the FWT layers and keep ensemble adaptors for cross-domain classification.